Choosing the correct wheel size is critical in B2B custom forged wheel projects. Incorrect specifications are often linked to fitment issues, delayed deliveries, and costly rework. This guide is written to standardize communication and reduce risk for buyers, dealers, and tuning companies.
Why Wheel Size Matters in Custom Forged Wheels
Wheel size defines fitment, performance, safety, and visual balance. In custom forging, every parameter is fixed by design. Once CNC machining starts, errors cannot be corrected without remaking the wheel.
For this reason, wheel size data must be accurate, complete, and verified before production.
1. Wheel Diameter

Definition
Wheel diameter is measured in inches across the bead seat.
Common Sizes
- Passenger cars: 17”–20”
- Performance & luxury: 19”–22”
- SUV & off-road: 18”–24”
Key Notes
- Larger diameters allow big brake clearance
- Ride comfort is reduced as diameter increases
- OEM brake and suspension limits must be respected
Diameter is usually determined first and should be confirmed with brake drawings.
2. Wheel Width
Definition
Wheel width is the distance between inner and outer bead seats.
Typical Widths
- Sedan: 7.5J – 9.5J
- Performance: 9J – 11.5J
- SUV / Off-road: 8.5J – 12J+
Key Notes
- Tire selection is restricted by wheel width
- Wider wheels improve grip but increase clearance risk
- Fender and suspension clearance must be checked
Width errors often lead to rubbing complaints after installation.
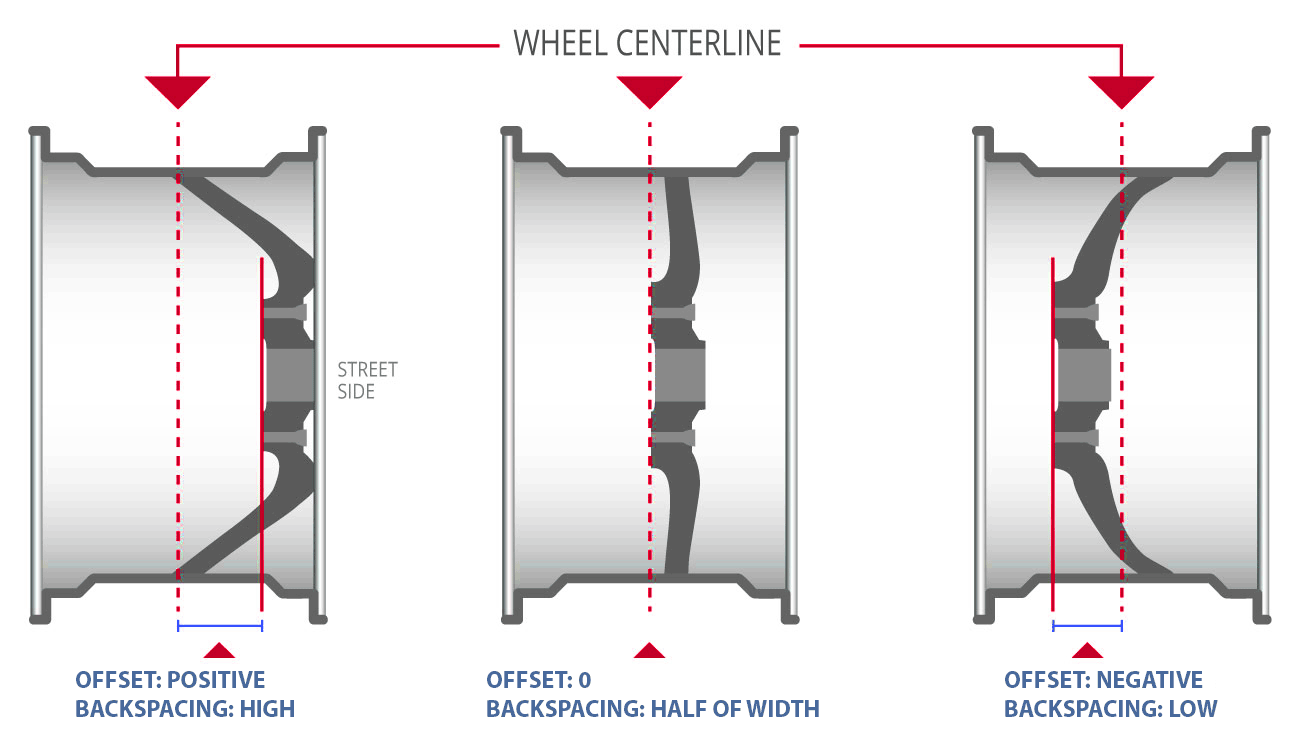
3. Offset (ET)
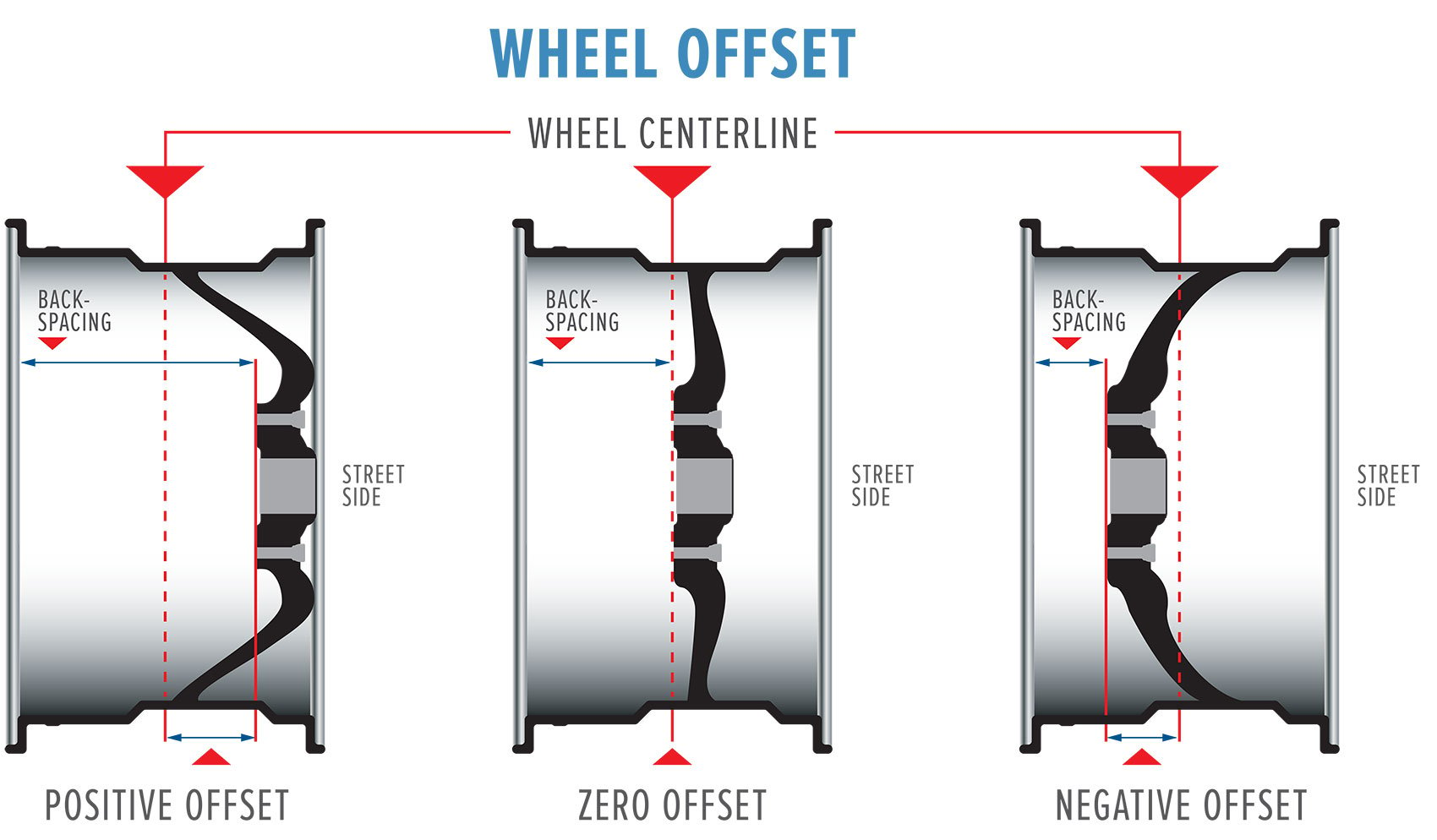
Definition
Offset is the distance (mm) between the wheel centerline and the mounting face.
Types
- Positive offset: wheel sits inward
- Zero offset: mounting face centered
- Negative offset: wheel pushed outward
Key Notes
- Incorrect offset causes suspension or fender contact
- Track width and steering geometry are affected
- Offset must match vehicle-specific data
Offset is one of the most critical parameters in custom forged wheels.
4. PCD (Pitch Circle Diameter)

Definition
PCD defines the number of bolt holes and the diameter of the bolt circle.
Examples
- 5×112
- 5×114.3
- 6×139.7
Key Notes
- PCD must match the hub exactly
- Adapters increase cost and complexity
- OEM specifications should always be verified
PCD mistakes make wheels impossible to install.
5. Center Bore (CB)
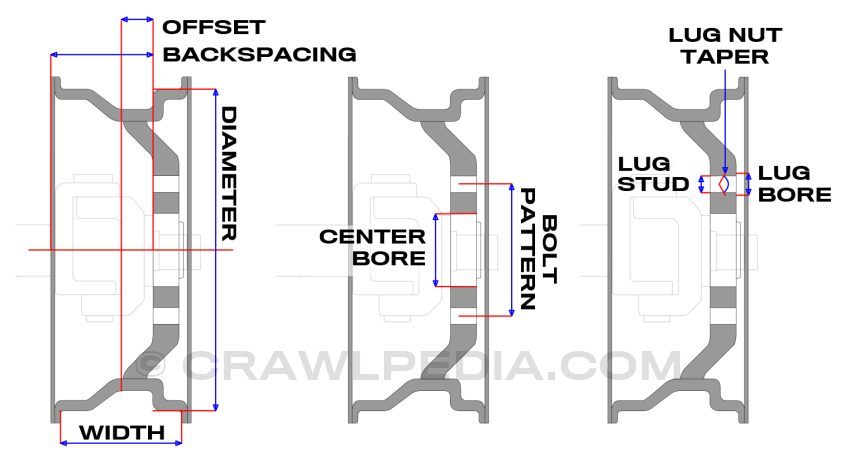
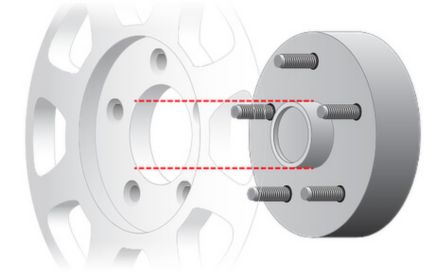
Definition
Center bore is the diameter of the wheel’s hub hole.
Key Notes
- Hub-centric fitment is strongly recommended
- Oversized CB requires hub rings
- Undersized CB cannot be corrected
Center bore accuracy ensures vibration-free driving.
Wheel Size Checklist for B2B Buyers
Before confirming production, the following data should be locked:
- Vehicle model & year
- Front & rear diameter and width
- Offset (ET) for each position
- PCD and bolt seat type
- Center bore requirement
- Brake clearance drawings
- Load rating target
Incomplete data is the most common cause of order delays.
Why Custom Forged Wheels Reduce Risk
Compared with cast wheels, custom forged wheels allow:
- Exact size control
- Vehicle-specific engineering
- Higher strength with lower weight
- Easier after-sales support
For B2B buyers, this results in fewer claims, fewer returns, and higher customer satisfaction.
Final Recommendation
Wheel size decisions should never be based on appearance alone. In professional projects, all parameters must be defined, reviewed, and confirmed before machining.
If uncertainty exists, it is recommended that drawings and vehicle data are reviewed with the manufacturer before order confirmation.
Need a verified wheel size solution for your next project?
Custom forged wheel specifications can be reviewed and optimized to match your vehicle, market, and performance goals.
